In the high-stakes world of biopharma, few stories are as compelling as the race to develop a successor to a multi-billion-dollar drug. We're joined today by Ivan Kairatov, a biopharma expert with deep experience in research, development, and the intricate dance between clinical data and commercial

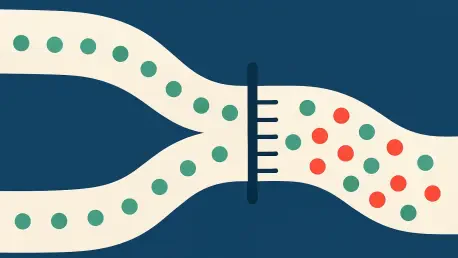
A groundbreaking collaborative study has revealed a critical vulnerability within the human immune system, uncovering a sophisticated mechanism of viral sabotage that fundamentally alters our understanding of how pathogens outsmart our natural defenses. Research has identified a single tissue

For millions of people who rely on proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to manage chronic acid reflux and other gastrointestinal conditions, a persistent concern has long cast a shadow over their treatment: the potential risk of developing stomach cancer. This decades-old question has fueled anxiety among
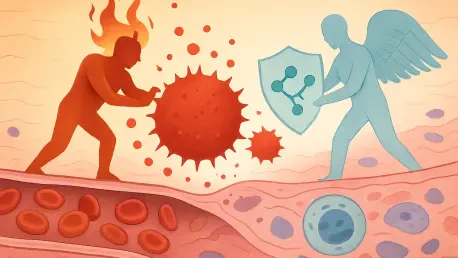
The same biological process that heroically defends the body against injury and infection can become a relentless saboteur when it fails to disengage, driving many of modern medicine's most formidable chronic diseases. For decades, the focus of anti-inflammatory treatment has been on suppressing

The arduous journey of a new drug from a laboratory concept to a patient's hands is a monumental undertaking, an odyssey fraught with staggering costs, extensive research, and an alarmingly high probability of failure. For every ten promising drug candidates that enter the rigorous phase of human

For the first time in over half a century, the fundamental list of nutrients considered indispensable for human life may be on the verge of a historic update, with the candidate being a familiar yet profoundly misunderstood dietary component. A concerted effort by leading nutrition experts is