
Beijing Huaguan Biotechnology Co., Ltd., a pioneering force in synthetic biology and green chemical manufacturing, has officially closed its Series C financing round, securing hundreds of millions of RMB to accelerate its growth trajectory. This substantial capital infusion was driven by a

In a move that sends ripples across the global pharmaceutical landscape, AstraZeneca has committed to a landmark $15 billion investment in China, a strategic initiative designed to run through 2030. The announcement, made on January 29, 2026, signals a profound deepening of the company's research,

For decades, the path from a promising antibody discovery in the lab to a life-saving therapy for patients has been fraught with uncertainty. Many drugs that show incredible potential in early tests ultimately fail in human trials, costing billions and delaying medical progress. Today we're
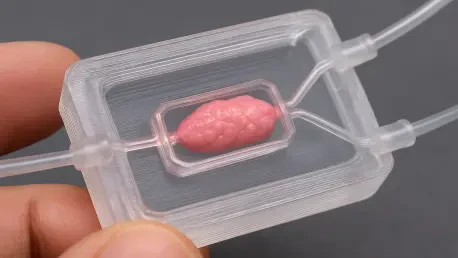
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking microfluidic chip using a single-step 3D printing process that successfully mimics the three-dimensional environments where cells grow in the human body, a development poised to revolutionize how diseases are studied and new drugs are tested. This new

For decades, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) was largely perceived as a threat to infants and the elderly. However, a seismic shift is underway, challenging this long-held view and repositioning RSV as a significant public health concern for a much broader adult population. Recent regulatory

The once-unbreakable bond between the United States and the World Health Organization has officially been severed, sending shockwaves through the global public health infrastructure and raising urgent questions about the future of international cooperation in an era of resurgent nationalism. This