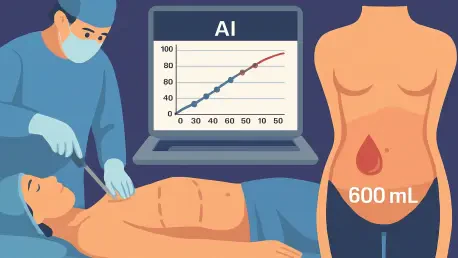
The world’s most popular cosmetic surgery now has a digital guardian, an intelligent algorithm designed to foresee its most significant complication before it even begins. Liposuction, a procedure sought by millions for aesthetic enhancement, carries inherent surgical risks that scale with the ambition of the procedure. A groundbreaking development in artificial intelligence now offers surgeons a highly accurate tool to predict blood loss, transforming a critical variable into a manageable factor and promising a new era of safety for patients. This innovation addresses the most pressing concern in high-volume procedures, shifting the paradigm from reactive management to proactive, data-driven planning.
Beyond Aesthetics Can We Predict the Biggest Risk in America’s Most Popular Cosmetic Surgery?
Liposuction is often perceived through the lens of its cosmetic benefits, yet beneath the surface lies the complexity of a major surgical intervention. While generally safe, the procedure’s primary risk is directly tied to the amount of tissue removed. As surgeons aspirate fat, a certain amount of blood is inevitably lost along with it. The central challenge for medical teams has always been the inability to precisely forecast this loss, relying instead on experience, patient observation, and generalized formulas that lack individual specificity.
This unpredictability creates a significant clinical hurdle, especially in cases where large volumes of fat are targeted. An underestimation of blood loss can lead to serious complications, including anemia, shock, or the need for emergency interventions. Conversely, an overestimation could result in unnecessary preparations, such as ordering blood products that go unused. This new AI model seeks to close that gap in knowledge, providing a patient-specific prediction that empowers surgeons with foresight.
The Hidden Danger in High-Volume Liposuction
The risk of significant hemorrhage escalates dramatically in what is known as large-volume liposuction (LAL). This category is typically defined as any procedure in which more than 4,000 milliliters of total aspirate (a combination of fat and fluid) are removed. In these extensive procedures, the potential for clinically significant blood loss becomes a primary concern that dictates much of the perioperative care, from intravenous fluid management to the availability of blood for transfusion.
The challenge is rooted in physiology. Each liter of fat removed contains a percentage of blood, and as the total volume increases, so does the cumulative loss. For the more than 2.3 million people who undergo liposuction annually, understanding this risk is crucial. The development of a predictive tool is therefore not just an academic exercise but a direct response to a clear and present need for enhanced safety protocols in this highly common procedure.
A Digital Revolution in the Operating Room
In a collaborative effort to mitigate this risk, researchers from the Mayo Clinic and the CIMA Clinic-Loja in Ecuador developed a sophisticated machine learning model. The project’s goal was to create an algorithm capable of learning the complex relationships between patient characteristics and surgical outcomes to generate a precise, individualized prediction of blood loss. This international partnership combined clinical expertise with data science to tackle a long-standing surgical challenge.
The AI was trained on a comprehensive dataset from 721 patients who had undergone LAL procedures at clinics in Colombia and Ecuador, all following identical surgical protocols to ensure data consistency. Researchers fed the algorithm a wide array of variables, including patient demographics, clinical measurements, and specific surgical details. After training the model on data from 621 patients, it was tested on a separate validation group of 100 patients, where it demonstrated a stunning 94% accuracy in predicting blood loss, with an average deviation of just 26 milliliters.
An Expert Consensus on a Groundbreaking Advancement
The medical community has recognized this development as a “groundbreaking advancement” for patient safety. The AI model serves as a powerful decision-support tool, augmenting a surgeon’s clinical judgment with a layer of objective, data-driven insight. Rather than relying solely on past experience or population averages, surgical teams can now enter a procedure with a highly reliable estimate of a key physiological response, enabling a more controlled and predictable operating environment.
This transition from estimation to prediction represents a significant leap forward. Researchers involved in the study emphasize that the potential for such AI applications in surgery is immense. By leveraging machine learning, the medical field can begin to anticipate and manage a host of surgical risks, moving toward a future where care is not only reactive but preemptive. This model is seen as a pioneering example of how technology can be integrated into clinical workflows to directly enhance patient outcomes.
Putting Prediction into Practice for a New Standard of Care
The practical applications of this AI tool are immediate and transformative. With an accurate prediction of blood loss in hand before the first incision, surgeons can proactively plan for necessary interventions. This includes arranging for blood transfusions in high-risk cases, optimizing intravenous fluid management to maintain stability, and making more informed decisions about the safe limits of fat removal for a particular patient.
This capability fosters a new standard of personalized surgical care. Instead of applying a uniform protocol to all LAL patients, surgeons can tailor their approach based on an individual’s predicted risk profile. This not only reduces the likelihood of complications but also enhances the process of informed consent. A surgeon can now have a more concrete discussion with a patient about their specific risks, backed by a data-validated prediction. The next step for researchers is to refine the model with a larger, more diverse global dataset, further increasing its accuracy and applicability.
The creation of this predictive AI model marked a pivotal moment in cosmetic surgery, demonstrating a powerful synergy between clinical medicine and data science. Its ability to provide surgeons with precise, patient-specific information fundamentally changed the approach to managing a critical surgical risk. This advancement not only enhanced the safety of a single procedure but also provided a compelling blueprint for the future of predictive analytics across all surgical specialties, where data-driven foresight became an indispensable tool for protecting patient well-being.