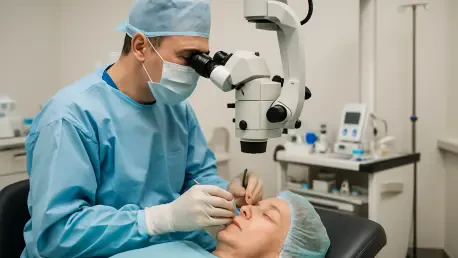
In a world where medical advancements are reshaping everyday procedures, consider the possibility of undergoing cataract surgery not in a daunting hospital setting, but in the familiar comfort of a doctor’s office, with just a simple pill to calm the nerves. This isn’t a far-fetched idea but a transformative reality gaining traction in ophthalmology. Millions of patients worldwide face cataracts, a leading cause of vision impairment, and the prospect of a less intimidating, more accessible surgery option is capturing attention. This shift promises to redefine how one of the most common surgeries is performed, blending convenience with cutting-edge care.
The significance of this development cannot be overstated. With an aging population and rising demand for efficient healthcare solutions, office-based cataract surgery using oral sedation offers a groundbreaking alternative to traditional hospital or ambulatory surgery center settings. Supported by compelling data and patient preferences, this approach addresses real challenges like anxiety, cost, and accessibility. It marks a pivotal moment in eye care, where innovation meets patient-centered design, potentially setting a new standard for surgical experiences across the field.
A New Era in Eye Care: Why Office-Based Surgery Matters
Office-based cataract surgery represents a bold departure from the norm, challenging the long-held assumption that complex procedures must occur in large medical facilities. The idea of walking into a familiar ophthalmologist’s office, taking an oral sedative, and undergoing surgery without the sterile, impersonal atmosphere of a hospital is reshaping patient expectations. This method prioritizes comfort and familiarity, reducing the psychological burden often associated with surgical environments.
Beyond emotional benefits, this shift also tackles logistical hurdles. Traditional settings often involve lengthy wait times, extensive pre-op preparations, and higher costs due to facility fees. Office-based surgery streamlines the process, allowing patients to receive care in a setting that feels more personal while maintaining rigorous safety standards. It’s a change that aligns with broader trends in healthcare toward minimizing patient stress and maximizing efficiency.
The Rising Demand for Improved Cataract Treatment
Cataract surgery remains among the most performed procedures globally, with millions undergoing the operation annually to restore vision. Yet, despite its prevalence, many patients face unnecessary obstacles in conventional hospital or ambulatory settings, from navigating complex scheduling to managing heightened anxiety. These challenges highlight the urgent need for a more approachable and cost-effective solution in eye care delivery.
A notable trend offers hope: over 100 private practices across the United States have already adopted office-based methods to meet this demand. This growing movement reflects a response to real-world issues, such as limited access to surgical centers in rural areas and the financial strain of hospital-based care. By rethinking where and how cataract surgeries are conducted, the field is moving toward greater inclusivity and patient satisfaction.
Understanding the Breakthrough: Oral Sedation in Office Settings
At the heart of this innovation lies the use of oral sedation, specifically diazepam in tailored doses—5 mg for older patients and 10 mg for younger ones—as a reliable alternative to intravenous methods. Research presented at a prominent ophthalmology meeting revealed striking results: only 10 percent of patients needed additional sedation, and a remarkable 99 percent chose the office setting for their second eye surgery when given the option. This predictability contrasts sharply with IV sedation, where variability can complicate the surgical process.
The approach is meticulously designed, with the timing of diazepam’s onset synchronized with pupillary dilation from eye drops, ensuring readiness for surgery. Purpose-built surgical suites further support this method, equipped with advanced air filtration, sterile processing areas, and specialized operating rooms. These facilities rival ambulatory centers in safety and functionality, demonstrating that office-based surgery is a carefully engineered solution, not a compromise.
This innovation also reduces the need for invasive monitoring, as oral sedation provides a steady, controlled effect. Unlike IV methods, where patients might enter surgery before sedation levels are confirmed, this protocol allows for precise assessment beforehand. Such efficiency underscores the potential for widespread adoption, as it aligns with the dual goals of patient safety and operational simplicity.
Insights from Experts and Patients in the Field
Feedback from practitioners who have embraced this method adds substantial credibility to its promise. A leading ophthalmologist, Dr. Brad H. Feldman, adapted to office-based surgery within days, noting that it offered unmatched comfort and safety for most patients compared to traditional settings. Large-scale studies, including those from Kaiser Permanente, further validate these observations, confirming the approach as a secure and effective alternative.
Patient experiences paint an equally compelling picture. Many express a clear preference for the office environment over ambulatory centers, citing reduced stress and the ease of a familiar setting. The ability to avoid the clinical atmosphere of larger facilities resonates deeply, with testimonials highlighting how a simple pill replaced the dread of needles and IV drips. These personal accounts underscore the human impact of this shift in practice.
Expert and patient perspectives converge on a shared conclusion: office-based cataract surgery with oral sedation isn’t just a technical advancement but a deeply personal improvement in care. The blend of empirical evidence and lived experiences illustrates a method that prioritizes both clinical outcomes and emotional well-being, paving the way for broader acceptance in the medical community.
Practical Steps for Embracing Office-Based Surgery
For ophthalmologists and patients considering this innovative approach, a clear path forward exists through structured implementation and informed decision-making. Accredited facilities are paramount, as seen in surgical suites like Dr. Feldman’s, which meet Joint Commission standards with dedicated operating rooms and advanced systems. Such infrastructure ensures that safety remains non-negotiable, even outside traditional hospital walls.
Sedation protocols also play a critical role, requiring careful assessment of patient readiness alongside pupillary dilation before surgery begins. Quick-dissolving tablets combining midazolam, ketamine, and ondansetron offer a backup if additional calming is needed, maintaining a seamless process. These practical measures demonstrate that the transition to office-based care is both feasible and meticulously planned for optimal outcomes.
Educational resources further support this shift, with courses at major ophthalmology meetings addressing practical, legal, and operational aspects of the method. These opportunities equip practitioners with the knowledge to integrate this approach responsibly while informing patients about their options. By fostering a culture of learning and collaboration, the field can ensure that this innovation reaches its full potential in transforming cataract care.
Reflecting on a Transformative Shift
Looking back, the journey toward office-based cataract surgery with oral sedation marked a significant turning point in how eye care was delivered. The compelling data, from minimal sedation needs to overwhelming patient preference, underscored a method that balanced efficiency with empathy. It was a moment when the field recognized that smaller, more familiar settings could deliver results on par with larger institutions.
As this approach gained traction, the focus shifted to actionable next steps. Ophthalmologists were encouraged to explore training programs and accreditation processes to adopt these practices safely. Patients, too, found empowerment in seeking out providers who offered this option, prioritizing comfort without sacrificing quality. The path ahead lay in continued research and shared experiences, ensuring that this innovation evolved into a cornerstone of modern eye care.