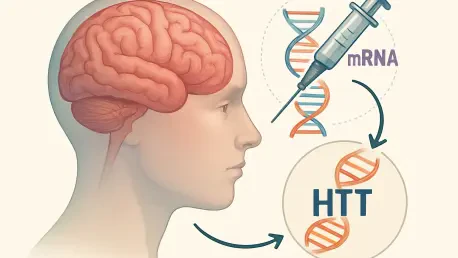
Imagine a world where a devastating, inherited brain disorder that robs individuals of their ability to move, think, and live independently could be slowed dramatically with a single medical intervention. Huntington’s disease, a fatal neurodegenerative condition caused by a defect in the HTT gene, has long been a source of heartbreak for families, with symptoms emerging in mid-adulthood and a life expectancy of just 10 to 30 years after diagnosis. Until now, no effective treatment existed to halt its relentless progression. However, a groundbreaking gene therapy known as AMT-130, developed by a pioneering company, offers a glimmer of hope. This innovative approach, involving intricate brain surgery to deliver custom DNA, aims to stop the production of the toxic huntingtin protein that damages neurons. Early trial results suggest a profound impact, potentially transforming the lives of those affected by this cruel disease.
Unveiling a Medical Milestone
Pioneering a Path with AMT-130
The development of AMT-130 marks a historic step forward in the battle against Huntington’s disease, a condition that has confounded medical science for decades. This gene therapy, designed to target the root cause by silencing the mutant huntingtin protein, requires a complex surgical procedure to inject tailored DNA directly into the brain. Conducted in the United Kingdom under the guidance of neuroscientist Ed Wild from University College London, the phase 1/2 clinical trial has captured global attention. With just one dose, the therapy holds the promise of a lifelong effect, a concept that was once unimaginable for such a progressive disorder. The trial’s early data, though not yet peer-reviewed, reveals staggering potential: at the highest dose, disease progression was slowed by up to 75 percent over a three-year period compared to untreated patients. This result stands as a testament to the power of genetic innovation in addressing previously untreatable conditions.
Measuring Success Through Biomarkers and Beyond
Beyond the headline figures, the trial’s impact is further evidenced by biological markers that paint a clearer picture of the therapy’s effect on the brain. In patients receiving the high dose of AMT-130, a significant reduction in a key biomarker of neurodegeneration was observed in their cerebrospinal fluid—a marker that typically rises as Huntington’s disease advances. This finding suggests that the therapy is not merely masking symptoms but altering the disease’s trajectory at a cellular level. Such a measurable change offers a concrete sign of hope for patients who have long faced an inevitable decline. Additionally, the trial’s design, involving 29 participants split between high and low doses, provides a robust framework for evaluating efficacy. The high-dose group’s slower progression over three years highlights a potential turning point, setting the stage for further studies to confirm these transformative outcomes across larger populations.
Looking Ahead to Transformative Care
Patient Stories Fueling Scientific Progress
The human element of the AMT-130 trial brings emotional depth to the scientific achievement, underscoring the real-world implications of this therapy. Among the 29 participants, personal accounts of improvement stand out, such as one individual who, after being medically retired due to the disease, returned to work following treatment. These stories reflect not just a slowdown in symptoms but a restoration of quality of life that many thought was lost forever. The courage of these patients, who underwent invasive brain surgery to advance medical knowledge, cannot be overstated. Their willingness to participate in such a novel procedure has paved the way for potential breakthroughs that could benefit countless others. As researchers continue to analyze the data, these individual experiences serve as powerful reminders of why such innovative treatments are worth pursuing with urgency and care.
Regulatory Momentum and Future Horizons
As the scientific community celebrates these initial findings, the path toward making AMT-130 widely available is gaining momentum with significant regulatory support. The therapy has earned designations such as Breakthrough Therapy and Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy from the FDA, signaling its priority status and the potential to expedite approval processes. Plans are in place to expand clinical trials across the US and Europe, while discussions with regulatory bodies and a Biologics License Application submission are targeted for early 2026. This rapid progression from preclinical research to human trials within a short span showcases a determined effort to bring relief to those in need. Reflecting on past steps, the collaboration between researchers, patients, and regulators proved instrumental in reaching this stage. Moving forward, the focus must shift to scaling access, ensuring affordability, and refining the therapy through additional data, all while maintaining the hope that this could redefine treatment standards for Huntington’s disease.